
Image Credit: NASA
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft has encountered several technical challenges that have impacted its missions. Notably, during a test flight in June 2024, the spacecraft experienced multiple issues, including thruster malfunctions and helium leaks. These problems led to the spacecraft returning to Earth without its intended astronaut crew, raising concerns about its reliability and future as a crew transport vehicle.

Image Credit: NASA
Thruster Malfunctions

During the June 2024 test flight, Starliner’s automated systems and astronauts conducting manual controls were prompted to repeatedly fire the Reaction Control System (RCS) thrusters. This rigorous testing revealed performance degradation in the thrusters, causing the spacecraft’s software to deem five of them as damaged and unusable. All five failed thrusters were aft-facing, resulting in a temporary loss of six degrees of freedom in attitude control until four were restored. Despite these challenges, the astronauts managed to safely dock the capsule to the International Space Station (ISS).
Helium Leaks
In addition to thruster issues, five separate helium leaks were detected in Starliner’s service module during the same test flight. Helium is crucial for pressurizing the spacecraft’s propellant tanks, and leaks can compromise the propulsion system’s efficiency and safety. These leaks contributed to NASA’s decision to abort the planned crew return using Starliner, opting instead to bring astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry “Butch” Wilmore back to Earth via SpaceX’s Crew Dragon in February 2025.
Impact on Astronaut Missions
The technical problems with Starliner led to significant mission adjustments. Astronauts Williams and Wilmore, initially scheduled for a brief mission, had their stay on the ISS extended to over nine months due to the spacecraft’s issues. They eventually returned to Earth safely aboard SpaceX’s Crew Dragon.
Boeing’s Response and Future Prospects
Boeing has been actively investigating the causes of these technical problems. Ground tests at the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico replicated the thruster degradation, linking it to a Teflon seal deformed by heat buildup. The company is working to address these issues to ensure the spacecraft’s reliability for future missions.
Despite these setbacks, NASA continues to support Boeing’s Starliner program, emphasizing the importance of having multiple commercial providers for crewed spaceflight to ensure redundancy and resilience in access to space.
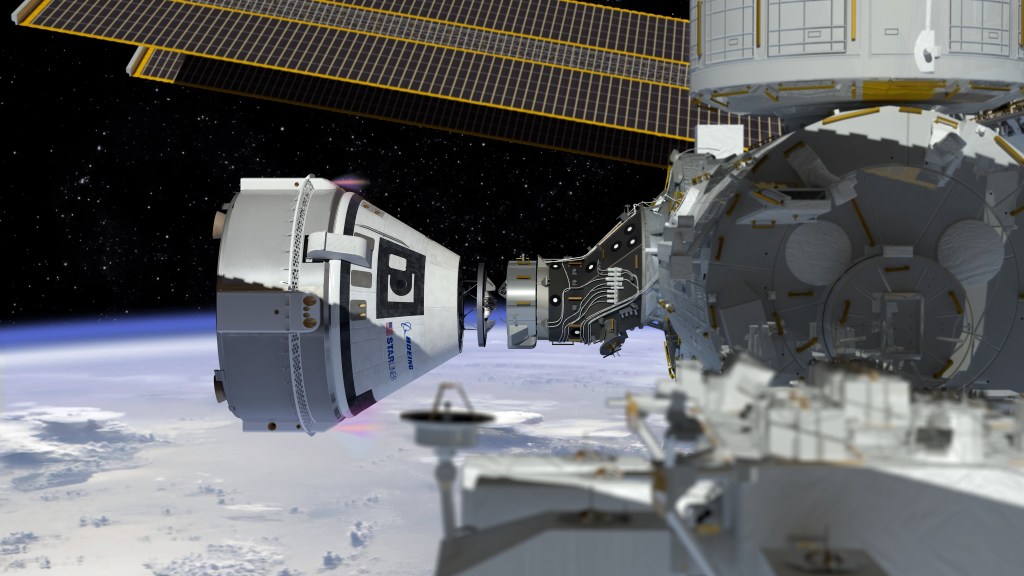
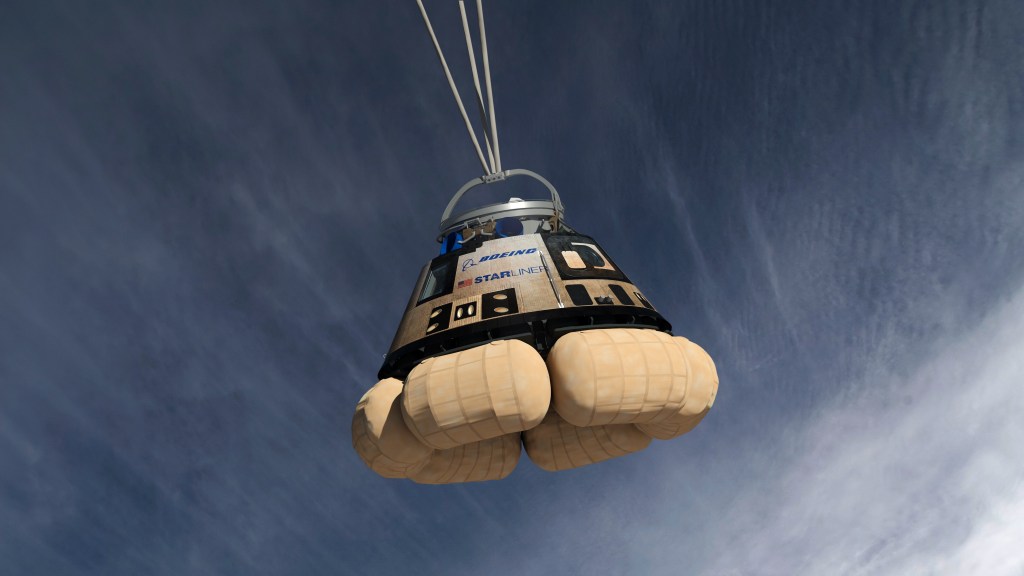


In summary, Boeing’s Starliner has faced significant technical challenges, including thruster malfunctions and helium leaks, leading to mission delays and adjustments. Ongoing investigations and corrective measures are crucial for the spacecraft’s future role in NASA’s crewed spaceflight missions.
Sources:
- NASA Decides to Bring Starliner Spacecraft Back to Earth Without Crew – NASA
- Boeing’s Crew Flight Test on Starliner Docks to Station – NASA
- Boeing’s Starliner Approaching Station Live on NASA TV – NASA
- NASA, Boeing Discuss Ground Testing, Forward Work for Starliner Return – NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test
Stay tuned for more updates on space missions and technological breakthroughs! If you’re passionate about space exploration, make sure to subscribe for more insights.
If you found this article interesting, you might also enjoy our deep dive into another fascinating topic!
Check out The Science Behind the Eiffel Tower’s Height Changes to learn how science affects iconic structures.

Leave a comment